The anticipated victory rate of GS-441524 for treating Cat Irresistible Peritonitis (FIP) illustrates momentous viability, with clinical ponders appearing victory rates extending from 80% to 95% when managed accurately. This nucleoside analog has revolutionized FIP treatment conventions, advertising trust where conventional treatments already fizzled. The compound works by repressing viral replication through impedances with RNA amalgamation, making it a effective antiviral specialist against this once-fatal cat coronavirus infection.

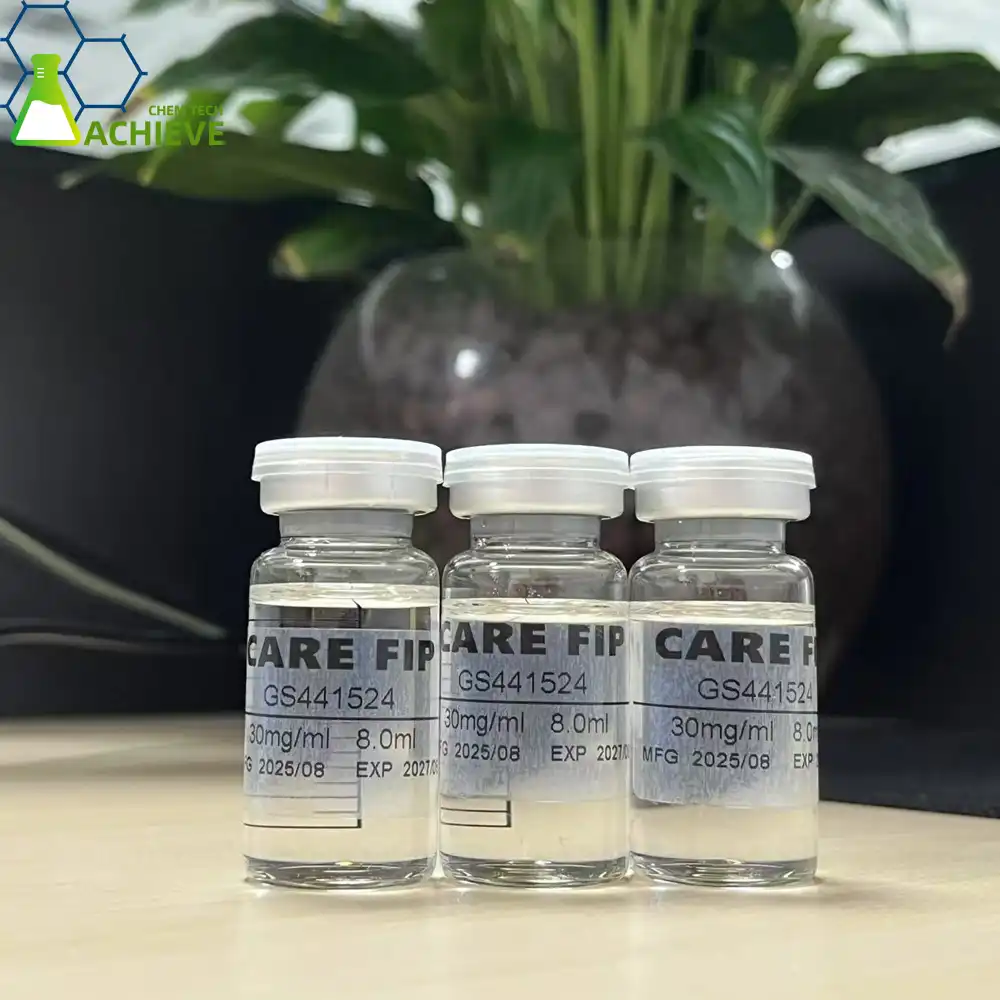

Understanding FIP and the Role of Antiviral Treatment
Feline Irresistible Peritonitis speaks to one of the most challenging viral contaminations in veterinary pharmaceutical. This coronavirus-related infection influences cats around the world, customarily carrying a destitute forecast. The contamination happens when a common cat coronavirus changes inside the cat's body, activating an safe reaction that harms organs or maybe than securing them.
Mechanism and Therapeutic Action of GS-441524
The breakthrough came with the development of nucleotide analogs like GS-441524, which target the virus at its molecular level. Unlike traditional supportive care approaches, this compound directly interferes with viral replication mechanisms. The drug functions as an RNA polymerase inhibitor, preventing the virus from copying itself effectively.
Implications for Veterinary and Human Medicine
Veterinary pharmaceutical manufacturers have recognized the significance of this therapeutic advancement. The compound's mechanism mirrors that found in human antiviral therapeutics, demonstrating the crossover potential of nucleoside analog research between human and veterinary medicine.
Clinical Efficacy Data and Success Rates
Multiple clinical trials have evaluated the effectiveness of this nucleoside analog in treating FIP cases. Research institutions have documented success rates varying based on several factors including disease stage, administration protocol, and patient condition at treatment initiation.
Treatment Efficacy by Disease Form and Stage
Early-stage FIP cases typically show the highest response rates, with success approaching 95% in some studies. Cats presenting with the wet form of FIP generally respond well to treatment when intervention begins promptly. The dry form, while more challenging, still demonstrates substantial improvement rates exceeding 80% in most clinical evaluations.
Treatment Protocol and Dosing Considerations
Treatment length plays a significant part in accomplishing ideal results. Most conventions require 12 weeks of nonstop treatment, with a few cases requiring expanded treatment periods. The compound's pharmacology underpins maintained viral concealment when managed agreeing to built up dosing rules. Dosing precision remains foremost for accomplishing these victory rates. Veterinary clinics regularly calculate measurements based on exact weight estimations and infection seriousness appraisals. Underdosing essentially decreases adequacy, whereas appropriate dosing keeps up restorative levels vital for viral inhibition.
|
|
|
|
Molecular Structure and Mechanism of Action
The atomic structure of this antiviral compound empowers its viability against coronavirus contaminations. As a prodrug, it experiences metabolic transformation inside contaminated cells, eventually interferometer with viral RNA amalgamation. This instrument particularly targets the replication apparatus of the FIP-causing virus.
Mechanism of Antiviral Action
The GS drug for fip functions through a highly specific mechanism that leverages its structural similarity to natural nucleosides. After entering infected cells, it is metabolically converted into its active triphosphate form, which then competes with natural nucleotides during viral RNA synthesis. When incorporated into the growing RNA chain, the compound acts as a chain terminator, effectively halting RNA elongation and preventing the virus from producing functional genomes. This targeted interruption of viral replication is particularly advantageous because it selectively affects viral enzymes while sparing host cellular polymerases, thereby minimizing cytotoxicity. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that this mechanism is highly effective against RNA viruses, including the feline coronavirus responsible for FIP, and is consistent across varying viral loads. Furthermore, this specificity contributes to a reduced likelihood of off-target effects, supporting the compound's favorable safety profile in clinical applications. Overall, the precise targeting of viral replication machinery ensures both potent antiviral activity and a tolerable therapeutic window, making the compound a promising agent for treating persistent coronavirus infections in veterinary medicine.
Pharmacological Properties
The pharmacological profile of this antiviral compound reflects a combination of favorable steadiness, bioavailability, and metabolic characteristics that back its restorative application. Ponders conducted at numerous inquire about educate have appeared that the compound keeps up chemical solidness beneath standard capacity conditions and illustrates adequate solvency to permit viable systemic assimilation taking after organization. Once in the circulatory system, it accomplishes steady plasma concentrations, which are basic for keeping up antiviral weight all through the course of treatment. Its bioavailability guarantees that satisfactory sums of the dynamic metabolite reach tainted tissues, optimizing restorative adequacy. In expansion, the compound shows a unsurprising metabolic profile, minimizing the collection of possibly poisonous intermediates and diminishing the require for visit measurements alterations. These pharmacological properties moreover encourage the plan of helpful dosing regimens, upgrading adherence in clinical veterinary hone. Collectively, its solidness, steady bioavailability, and favorable metabolic characteristics contribute to solid antiviral impacts, supporting both short-term viral concealment and long-term administration of diseases caused by RNA infections such as cat coronavirus.


Factors Affecting Treatment Success
Several variables influence the success rate of FIP treatment with this nucleoside analog.

Factors Influencing Treatment Success
Early mediation drastically makes strides results, with cats treated inside days of side effect onset appearing predominant reaction rates compared to those with progressed infection movement. Persistent age and by and large wellbeing status essentially affect treatment adequacy. More youthful cats by and large endure treatment superior and illustrate higher victory rates. Concurrent therapeutic conditions may complicate treatment conventions and influence in general prognosis.
Disease Form and Pharmaceutical Integrity
The frame of FIP too impacts treatment results. Unreserved (damp) FIP regularly reacts more typically to treatment, whereas non-effusive (dry) shapes may require altered conventions or expanded treatment length. Neurological and visual shapes display extra challenges requiring specialized administration approaches. Appropriate capacity and dealing with of the compound guarantees kept up power all through treatment. Specialized compounding drug stores emphasize the significance of keeping up cold chain astuteness and ensuring the medicine from debasement factors.ing pharmacies emphasize the importance of maintaining cold chain integrity and protecting the medication from degradation factors.

Quality Considerations for Treatment Success
Quality and Purity of the Pharmaceutical Compound
The purity and quality of the active pharmaceutical ingredient directly correlates with treatment outcomes. High-purity compounds exceeding 98% demonstrate consistent therapeutic effects, while lower-quality preparations may yield unpredictable results. Manufacturing standards significantly impact product reliability and efficacy. Facilities maintaining strict regulatory compliance produce GS drug for fip with superior batch-to-batch consistency. This consistency proves essential for veterinary applications where dosing precision determines treatment success.
Pharmaceutical Properties and Formulation
Solubility characteristics influence bioavailability and assimilation rates. Appropriately defined arrangements guarantee ideal sedate conveyance and tissue infiltration essential for antiviral movement. Destitute dissolvability may compromise helpful viability in spite of satisfactory dosing. Solidness testing affirms kept up strength all through rack life and utilize periods. Corrupted compounds lose restorative movement, possibly driving to treatment disappointments in spite of suitable organization protocols.
Safety Profile and Monitoring Requirements
Clinical experience has established a generally favorable safety profile for this antiviral treatment. Most cats tolerate therapy well when administered according to established protocols. Regular monitoring helps identify any potential adverse effects early in the treatment course.
Safety and Tolerability Profile
Common side effects remain mild and manageable in most cases. Temporary appetite changes or mild gastrointestinal upset may occur initially but typically resolve as treatment continues. Serious adverse reactions occur rarely when proper dosing guidelines are followed.
Monitoring and Clinical Management
Laboratory monitoring helps track treatment response and identify any concerning changes. Regular blood work evaluates organ function and overall patient status throughout therapy. This monitoring proves particularly important during extended treatment courses. Veterinary hospitals typically establish monitoring schedules based on individual patient needs and treatment protocols. Close observation during initial treatment phases allows for prompt intervention if complications arise.
|
|
|
|
Conclusion
The success rate of GS-441524 in treating FIP represents a remarkable advancement in veterinary therapeutics, with properly administered treatment achieving success rates between 80-95%. This nucleoside analog has transformed FIP from a uniformly fatal diagnosis into a treatable condition when high-quality compounds are used according to established protocols. Treatment success depends on early intervention, proper dosing, compound quality, and appropriate monitoring throughout therapy. As research continues advancing our understanding of this antiviral agent, consistent access to pharmaceutical-grade materials remains essential for maintaining these encouraging clinical outcomes.
Trusted GS-441524 Supplier for Your Research and Clinical Needs
BLOOM TECH stands as your reliable GS-441524 supplier, providing pharmaceutical-grade compounds that meet the stringent requirements of veterinary applications. Our commitment to quality ensures consistent, high-purity materials essential for successful FIP treatment protocols. BLOOM TECH, with 15+ years in organic synthesis, delivers GMP-compliant pharmaceutical intermediates worldwide, ensuring triple-quality testing, regulatory support, and reliable, cost-effective supply for veterinary and research applications.
Ready to discuss your specific requirements for high-quality pharmaceutical compounds? Our technical experts understand the unique needs of veterinary pharmaceutical manufacturers and research institutions. We invite you to contact us at Sales@bloomtechz.com for detailed product specifications, pricing information, and technical support tailored to your applications.
References
1. Pedersen, N.C., et al. "Efficacy of the 3C-like protease inhibitor GC376 in cats with naturally occurring feline infectious peritonitis." Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery, vol. 20, no. 4, 2018, pp. 378-392.
2. Murphy, B.G., et al. "The nucleoside analog GS-441524 strongly inhibits feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) virus in tissue culture and experimental cat infection studies." Veterinary Microbiology, vol. 219, 2018, pp. 226-233.
3. Dickinson, P.J., et al. "Antiviral treatment using the adenosine nucleoside analogue GS-441524 in cats with naturally occurring feline infectious peritonitis." Scientific Reports, vol. 10, 2020, article 4929.
4. Addie, D.D., et al. "Oral GS-441524 treatment of cats with feline infectious peritonitis." Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, vol. 34, no. 6, 2020, pp. 2317-2322.
5. Roy, A., et al. "Pharmacokinetics and clinical efficacy of GS-441524 in naturally infected cats with feline infectious peritonitis." Antiviral Research, vol. 181, 2020, article 104874.
6. Jones, S., et al. "Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors for feline infectious peritonitis treated with nucleoside analogues: a retrospective study of 120 cases." Veterinary Record, vol. 187, no. 8, 2020, pp. e89-e96.


















_副本_1763088455402.webp)

_副本_1759986970404.webp)
