GS-441524 and Remdesivir: Understanding Their Connection
Chemical Structures: Similarities and Differences
Two substances, GS-441524 fip and Remdesivir, have attracted a lot of interest in the field of antiviral research. A remarkable biochemical relationship exists between these molecules, and it has far-reaching consequences for the fields of veterinary and human medicine. The veterinary use of GS-441524 has been revolutionised, thanks to its function in treating Feline Infectious Peritonitis (FIP). As one of the first antiviral treatments to get FDA approval, Remdesivir came to the forefront during the COVID-19 pandemic after being created specifically for human use. While their variations in approved status and use bring up significant ethical and regulatory concerns, their structural similarities underscore the possibility of cross-species therapeutic discoveries. Exploring their chemical structures, therapeutic uses, and the ever-changing regulatory environment, this article dives into the complex link between these molecules and how they are shaped by medicine.
|
|
|
Chemical Structures: Similarities and Differences
Molecular Foundations
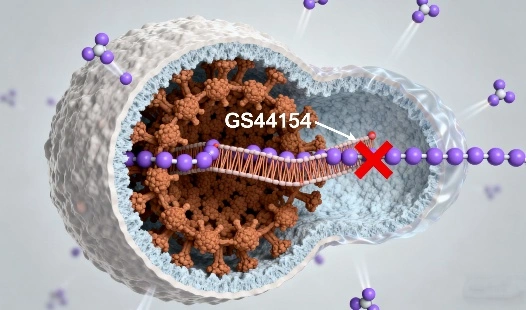
GS-441524 and Remdesivir are closely related compounds, with GS-441524 serving as the primary metabolite of Remdesivir. Both molecules belong to the nucleoside analog class, which are specifically designed to interfere with viral replication processes by mimicking natural nucleotides. Once incorporated into the viral RNA chain, these compounds disrupt the virus's ability to reproduce effectively, ultimately halting the spread of infection within the host. GS-441524 has gained recognition in veterinary medicine, particularly for treating Feline Infectious Peritonitis (FIP), while Remdesivir has been developed and authorized for use in humans, most notably during the COVID-19 pandemic. Their close biochemical relationship highlights the value of shared antiviral mechanisms across different species and therapeutic contexts.
Structural Nuances
While sharing a common core, these compounds differ in their chemical modifications:
- GS-441524: A simpler structure, lacking the phosphate group present in Remdesivir.
- Remdesivir: Contains an additional phosphate group, which is cleaved in vivo to form GS-441524.
Implications of Structural Differences
The structural variations between these compounds influence their:
- Cellular uptake
- Metabolism
- Antiviral efficacy
 |
 |
 |
From Feline to Human Medicine: Crossover Potential
Veterinary Applications
GS-441524 has shown remarkable efficacy in treating feline infectious peritonitis (FIP), a previously fatal disease in cats. Beyond discussions about the GS-441524 price, its clinical success has generated strong interest in its potential applications in human medicine, especially given its close structural similarity to Remdesivir, a drug already used in treating viral infections such as COVID-19. Researchers are intrigued by the possibility that GS-441524's antiviral mechanisms, which involve inhibiting viral RNA replication, could extend beyond feline diseases and offer therapeutic benefits for human viral illnesses as well. Although much of the evidence is currently limited to veterinary studies, the promising outcomes in cats have laid a foundation for future exploration, potentially opening new doors in antiviral drug development.
Human Medicine Prospects
Remdesivir, initially developed for human use, has demonstrated efficacy against various viral infections, including:
- SARS-CoV-2
- Ebola virus
- Other coronaviruses
Comparative Efficacy
Research suggests that GS-441524 may offer advantages over Remdesivir in certain scenarios:
- Improved cellular penetration
- Potentially fewer side effects
- Simplified administration
Why Regulatory Approval Matters?
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape
The path to regulatory approval for these compounds differs significantly:
- Remdesivir: FDA-approved for human use in treating COVID-19
- GS-441524: Currently lacks formal approval for veterinary or human use
Implications for Research and Development
The regulatory status of these compounds impacts:
- Availability for clinical trials
- Funding for further research
- Potential for widespread clinical application
Future Prospects
As research progresses, the regulatory landscape for GS-441524 may evolve, potentially opening new avenues for its use in both veterinary and human medicine.
Conclusion
Synergistic Potential
The connection between GS-441524 and Remdesivir exemplifies the intricate relationship between veterinary and human medicine. By studying how these two compounds function individually and in relation to one another, researchers are uncovering valuable insights into cross-species antiviral strategies. Their complementary mechanisms highlight the possibility of developing treatment pathways that serve both human and animal health. This synergy reflects a growing recognition that breakthroughs in veterinary science can inform human medicine, ultimately paving the way for more innovative, wide-reaching therapeutic solutions.
Ongoing Research
Scientists continue to explore the unique properties of GS-441524 and Remdesivir with great interest. Current studies focus not only on improving their antiviral potency but also on optimizing dosing regimens, delivery methods, and safety profiles across species. The goal is to expand their potential applications beyond existing uses and address a wider range of viral diseases. As research progresses, these efforts could yield new strategies for managing viral outbreaks, strengthening preparedness for future pandemics, and enhancing therapeutic options in both human and veterinary contexts.
|
|
|
FAQ
1. Q: How does GS-441524 differ from Remdesivir in terms of efficacy?
A: While both compounds show antiviral activity, GS-441524 may offer improved cellular penetration and potentially fewer side effects compared to Remdesivir. However, more research is needed to fully understand their comparative efficacy across different viral infections.
2. Q: Is GS-441524 approved for use in humans?
A: Currently, GS-441524 is not approved for human use. It has shown promise in veterinary applications, particularly in treating feline infectious peritonitis, but requires further research and regulatory approval for human medical use.
3. Q: What factors influence the GS-441524 price?
A: The GS-441524 price is influenced by various factors, including production costs, research and development expenses, regulatory status, and market demand. As it is not yet approved for widespread use, pricing may fluctuate based on availability and ongoing research needs.
Call to Action
Would you want to learn more about the possibilities of GS-441524 as a researcher or a veterinarian? The GS-441524 is a high-quality research instrument offered by Shaanxi BLOOM TECH Co., Ltd. We guarantee the consistency and purity of our goods with clear information on the GS-441524 price, in addition to our state-of-the-art GMP-certified facilities and stringent quality control systems.
If you want comprehensive technical data or analytical certifications, our team of specialists is here to help. Our dedication to providing you with reasonable pricing and effective logistics stems from our understanding of the critical role that dependable supply chains play in driving scientific research forward.
Take the next step in your antiviral research. Contact us today at Sales@bloomtechz.com to discuss your GS-441524 requirements and how we can support your research goals.
References
1. Murphy, B. G., et al. (2020). "The nucleoside analog GS-441524 strongly inhibits feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) virus in tissue culture and experimental cat infection studies." Veterinary Microbiology, 219: 226-233.
2. Sheahan, T. P., et al. (2017). "Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses." Science Translational Medicine, 9(396): eaal3653.
3. Warren, T. K., et al. (2016). "Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys." Nature, 531(7594): 381-385.
4. Yan, V. C., & Muller, F. L. (2020). "Advantages of the Parent Nucleoside GS-441524 over Remdesivir for Covid-19 Treatment." ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 11(7): 1361-1366.

Echo
9 years of experience in chemical articles; Doctoral degree; Organic Chemistry major; R&D-4 Dept; Technology support; R&D engineer
Anticipating your Business & Technology support inquiry
Please send us the products that interest you, and we will provide you with one-on-one service
Recommended Blog

How to Tell if Your Cat is Fully Cured After GS-441524 Treatment?

How is GS-441524 administered, and what are its side effects?

How to Handle Painful GS-441524 Injections: 5 Tips to Ease Your Cat's Stress

GS-441524 Injection Site Issues: What to Do About Redness and Lumps?

What Are the Side Effects of GS-441524? And How to Manage Them Effectively?